
Empathy



Psychosynthesis is a holistic approach to psychology, developed by Roberto Assagioli (1888-1974) that incorporates psychoanalysis, but significant transcends it by emphasizing health, development, and spirituality. Assagioli illustrated his view of the human psyche in his “egg-diagram” (see Figure) with seven elements:
Figure. Assagioli’s Egg Diagram
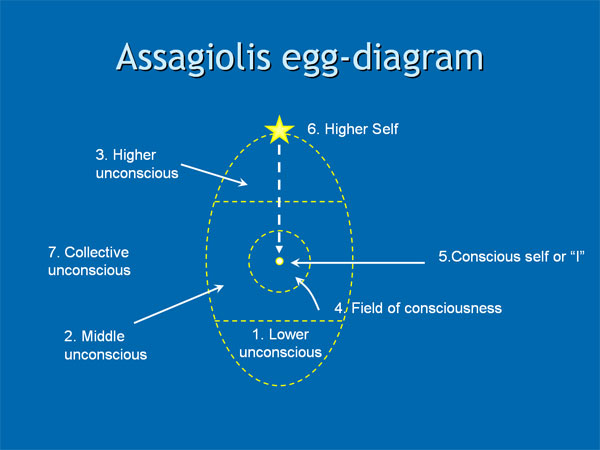
Source: Kenneth Sorensen, https://kennethsorensen.dk/en/. Used with permission.
1. The Lower Unconscious
The lower unconscious, according to Assagioli, contains the basic psychological activities that conduct the operative and intelligent coordination of the body and bodily functions. This dimension of the psyche also holds one’s foundational drives and animalistic urges, as well as emotionally intense established thematic patterns (i.e., psychological complexes), dark dreams and fantasies, and some pathological disturbances such as paranoid delusions, uncontrollable urges, obsessions, and phobias.
2. The Middle Unconscious
The middle unconscious, according to Assagioli, includes psychological dimensions comparable to waking consciousness with ready access to it. Life experiences are integrated, and standard cognitive and creative intelligence activated in a type of psychological incubation before entering the field of conscious awareness.
3. The Higher Unconscious or Superconscious
The higher unconscious or superconscious is the region that holds our highest inspirations, aspirations, and intuitions for ourselves, humanity, and our world. This realm is also the source of our higher emotions such unconditional love and higher intelligences. It also holds the deeper experiences of insight, contemplation, and bliss, as well as potentials for higher spiritual experiences and psychic abilities.
4. The Field of Consciousness
For Assagioli, the field of consciousness, a term he thought useful but not quite precise, referred to the part of our personality of which we are conscious, including the thoughts, bodily sensations, emotions, desires, and impulses we are able to see and evaluate.
5. The Conscious Self or “I”
The conscious self or “I” is the term Assagioli used to refer to the “the point of pure-awareness,” not to be confused with the field of consciousness highlighted above, which refers to the content of experience. The conscious self or “I” refers to the experiencer. He compared the “I” to a projector light and field of consciousness to a screen onto which images are projected.
6. The Higher Self
Unlike Freud’s psychoanalysis, which only includes a lower unconscious, Assagioli’s psychosynthesis includes the Higher Self or soul depicted above the conscious self in the egg diagram. According to Assagioli, one can experience the Higher Self through the use of psycho-spiritual practices such as meditation.
7. The Collective Unconscious
Assagioli’s collective unconscious, similar to Jung’s conceptualization of the term, refers to universal, nonpersonal common forms or archetypes that surround and influence us on a collective level. Assagioli distinguished between primitive, archaic forms and higher, progressive forces of a more spiritual nature.
Although not depicted in Assagioli’s original egg diagram (though some contemporary illustrations do include it), another key element of psychosynthesis is the concept of subpersonalities. Subpersonalities, similar to Jung’s persona, refers to parts or formed habit patterns in the human psyche, conscious and unconscious, that we repeatedly express in our lives. For the healthy person, subpersonalities are conscious and in the field of self-awareness and self-regulation. In psychosynthesis, subpersonalities may reside in the lower, middle, or higher unconscious, unlike Jung’s persona or false self. Additional fundamental concepts of psychosynthesis, which highlight stages of Self-realization, include self-knowledge, self-control, disidentification, unifying center, and psychosynthesis, as the peak stage in his model.
Disidentification refers to the necessity of separating oneself (the conscious I) from overidentification with everything outside or beyond oneself. Overidentification can happen any time we identify with an aspect of our life experiences such as a subpersonality, our ethnicity, fear, anxiety, or a role to such an extent that it dominates our lives. Thus, healing and growth opportunities lie in seeing when and where one overidentifies and, with the help of exercises and practices, severing the control of the overidentification on oneself or “I.”
Over time, former objects of overidentification can be healthily integrated into the middle unconscious and accessed more intentionally. The unifying center refers to the discovery or creation of an ideal around which one can reach or reorganize one’s life. Psychosynthesis, in addition to referring to Assagioli’s entire approach to psychotherapy, refers to the peak of the developmental process that establishes a new personality around a primary unifying center: one that is “coherent, organized and unified” (2000, p. 23).
Consequently, personal will (the Will) is a highly significant concept in psychosynthesis such that Assagioli dedicated a book on the topic entitled, The Act of Will. The will is an element of Assagioli’s Star Diagram of Six Psychological Functions (see Figure 5-2/Not included in this essay), which he developed later in his life to complement the egg diagram of the psyche. Lamenting the state of psychology in 1958, Assagioli is quoted as stating, “After losing its soul, psychology lost its will, and only then its mind and senses” (2007, Foreword).
Furthermore, Assagioli held the view of the existence of a transpersonal will, which he viewed as a dormant potentiality for most people. Assagioli’s transpersonal will aligns with what Maslow referred to as “higher needs” and the growing field of transpersonal psychology refers to using a variety of terms that include Christ consciousness, unitive consciousness, peak experiences, mystical experiences, spirit, oneness, and other such similar concepts.
As mentioned above, psychosynthesis proposes a dynamic five-stage healing and realization process (see Table—Not included in this essay). Stage zero highlights the predominate stage of humanity, characterized by what Assagioli called, the “fundamental infirmity of man.” John Firman (?–2008) referred to this human condition as “primal wounding”; wounding resulting from not being seen and heard for who we truly are by significant others in our lives. Stage 1 relates to the tuning in of one’s inner experience and the cultivation of greater self-awareness. Self-awareness is the foundation of all growth and development. Without self-awareness, we tend to react out of instinct and habitual responses or what Firman referred to as, the survival personality. As self-awareness expands, we start to see our tendencies, preferences, and shortcomings.
Eventually, we (often with the help of supportive practices or a skilled guide) begin to free ourselves or disidentify from our habitual thoughts, feelings, reactions, and roles, thereby cultivating the witness or individual observer “I” (Stage 2). Over time, we may start sensing a more expansive identity or connectedness to life and begin to feel new vocational urges, creative impulses, or directive promptings (Stage 3). From a psychosynthesis perspective, this involves surrendering and inviting a more intimate, conscious relationship with the Highest Self or soul. The fourth stage of psychosynthesis corresponds to a period in which we are formally responding to the invitations of the Highest Self (in contrast to the personal self or ego in its contemporary usage) and developing more spiritually.
Survival of wounding, exploration of the personality, the emergence of I, contact with the Highest Self, and response to the Highest Self represent the five stages of psychosynthesis. However, Assagioli and others (e.g., Firman & Gila, 2002 and Brown, 2009) cautioned that these stages do not represent a set developmental sequence, but potential responses to the human condition that can occur at any age.
It is important to note that Assagioli presented psychosynthesis in two subcategories: personal psychosynthesis and transpersonal psychosynthesis. The emphases of personal psychosynthesis are self-awareness and self-regulation. The foci of transpersonal psychosynthesis are on the realization of one’s Highest Self/soul and the actual psychosynthesis, the reformation of the personality around a new unifying center or ideal.
Numerous practices and exercises align with psychosynthesis overall and in these two categories. Thus, to identify a narrow set of core practices is inconsistent with this reality. However, it is fair to say that visualization, drawing, self-observation, and meditation are common practices among psychosynthesis-oriented counselors, therapists, and coaches. In addition, as highlighted above, disidentification is a core concept of psychosynthesis and activities aimed at freeing oneself from overidentifying with a dimension of our being or life other than the center of pure awareness or “I.”
Given today’s pressing global challenges and the subsequent demands on human beings, psychosynthesis offers a holistic and hope-filled paradigm for the journey toward healing, well-being, self-actualization, and Self-realization.
Note: Modified excerpt from my book, “Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders”

Greetings! I am excited to share that excerpts from the new audiobook version of Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders are now available on my new YouTube Channel. I invite you to check one of my first offerings:
After the recent (September 2018) United States Senate Judiciary Committee voted to advance Brett Kavanaugh’s Supreme Court nomination to a full Senate vote, Senator Kamala Harris from California declared that Republican senators relied on “raw power” to push the nomination forward. While Kavanaugh ended up securing the Senate votes needed to fill the US Supreme Court seat, the degree of concurrence with this assessment of Senate Republicans (and Kavanaugh himself) indicate that change is in the air.
Change is in the air because this type of raw power or power over has been the norm of Western Civilization for eons. This history of power over includes the domination and objectification of women which was clearly on full display in the Kavanaugh drama as well. It was deeply painful for many women and men to witness this public display and “victory” of power over leadership. After all, haven’t Americans evolved as a people? How could this and so many other blatant displays of power over leadership succeed in 2018?
I admit to periodic despair and dismay over these failings of leadership. However, a growing number of people are rejecting power over leadership for a new way—leadership as power to and with. Power to and with occurs when individuals claim what the Native peoples of the American continents, according to anthropologist, author, and educator, Angeles Arrien (1940 -2014) refer to as “original medicine” or their unique authentic inner power.
 As we claim our authentic inner power, we free and fuel ourselves to genuinely express our deepest yearnings not only for ourselves but also for our world. We are then able to move into power with relationships as we join in cooperative partnerships with others for a more equitable, inclusive, peaceful, and sustainable world for all.
As we claim our authentic inner power, we free and fuel ourselves to genuinely express our deepest yearnings not only for ourselves but also for our world. We are then able to move into power with relationships as we join in cooperative partnerships with others for a more equitable, inclusive, peaceful, and sustainable world for all.
For example, the current “Me Too Movement” which is bringing growing awareness of and action on sexual harassment and sexual assault against women, began in 2006 when Tarana Burke, an American community organizer, began using the phrase “Me Too” to bring attention to the severity of these social ills. Burke’s power to authentically self-express ignited a spark within American actress Alyssa Milano, who then used the term on the social media platform Twitter in 2017.
These two women claimed their power to authentic self-expression which has inspired thousands of women and men, celebrities and noncelebrities, to express power with one another to build an impactful movement. For example, the Me Too Movement has resulted in change within various sectors of American society, particularly the corporate media sector (e.g., firing and/or legal action against film producer and Miramax cofounder, Harvey Weinstein; CBS Corp. Chairman and CEO Les Moonves; NBC “The Today Show” anchor Matt Lauer, and CBS anchor Charlie Rose).

Further indications of this emerging new way of leading can also be seen in a growing body of academic and popular literature on this power to and with orientation such as feminine leadership, compassionate leadership, and participatory leadership. In addition, my 2015 doctoral research, which I highlight in my book, Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders, identified integrated or balanced leadership as the primary developmental theme of mindful leaders. Integrative/balanced leadership is the term I chose to describe their shift from heavily weighted traditional masculine expressions of leadership to more balanced expressions of traditional feminine and masculine qualities.
Consequently, despite the darkness of our times and the onslaught of gross displays of raw power spewed from high places, there are countless people, women and men, across the globe building a new way of leading from power over to power to and with. You too can contribute to this emerging expression of leading by engaging in a personal transformative journey that connects you with your authentic inner power and fosters an expansion of consciousness and heart our nations, world, and planet Earth so desperately needs.
For fellow bloggers interested in mindful leadership, leader development, and self-transformation, I invite you to check out my new book, “Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders” now available from Amazon in Kindle and paperback versions.

When written in Chinese, the word ‘crisis’ is composed of two characters. One represents danger and the other represents opportunity. John F. Kennedy
As emphasized in the management literature, employees frequently resist organizational change for a variety of reasons to include fear of the unknown. As we all know from our own lives, resistance to change also occurs on the individual level as well as the organizational level. Consequently, individuals and collectives tend to be more open to learning and growth opportunities when they are faced with a personal or professional crisis. When a personal and professional crisis propels a leader to move into unknown territory in and through constructive action, it can serve as a transformative learning opportunity.
Transformative learning occurs when radically new experiences induce a tectonic shift in perspective in the way one views him/herself, others, and the world. Longtime leadership scholar and author, Warren Bennis refers to these types of transformative events as crucibles. He and co-author Robert Thomas wrote in their seminal article on the topic that highly effective leaders are the people who can find meaning in and learn from their most painful and difficult crucibles. Such leaders emerge from the ashes more confident, strong, and more committed to the things that deeply matter to them.
Effective leaders that use their crucibles as learning opportunities have growth mindsets. In her work on mindsets, Carol Dweck makes the distinction between fixed and growth mindsets. Leaders with fixed mindsets view themselves and others as being born with a limited amount of capacity and potential for learning. Thus, the emphasis is on protecting their image and proving themselves. From the fixed mindset, failure is feared and avoided at all costs.
In stark contrast, leaders with growth mindsets hold the view that they and others can build upon the capacities they with which they were born. They see failure as a natural and welcomed dimension of learning and development. Leaders with a growth mindset also know that success does not simply happen to them. They celebrate that success (as they define it) requires passion, effort, training, and yes, failure. The growth mindset is illustrated in the stories shared by the mindful leaders interviewed for my 2015 study (insert link).
At the time, I was really struggling with depression and anxiety, and it had been recommended for me to take that (Mindfulness Based Stress Reduction) class. And the unexpected side effect was the really powerful impact of helping me create a daily mindfulness practice, which for me is a combination of meditation, daily taking time out for just mindfulness moments, trying to do things in general, everything I do, more mindfully, being more aware of it. (Female middle manager and marketing researcher)
But in terms of my more recent delving into it (mindfulness), it’s been maybe about 3 years, 2 and a half to 3 years where I’ve been seriously getting into meditation, and to be perfectly honest with you, what prompted me was my wife’s illness and being able to get myself to a place of being able to deal with and handle that. The self-awareness, the centeredness, the calm, the ability to sort of control the uncontrolled, I think were the more attractive things about it and just not only that, the relieving of stress was one of the things that attracted me to it, ‘cause I was undergoing a lot of stress and I felt like I needed to get a handle on it. I exercise, I walk, I do those things, but you know, I felt that there was a, maybe a better way to attain that, I think, so yeah. (Male senior manager and administer in higher education)
Thus, leaders yearning to be and become more self-aware and effective turn their crises into opportunities for constructive action. By choosing growth mindsets over fixed mindsets, they open themselves to unforeseen possibilities that alter their lives in powerful and profound ways. So, next time you face a personal or professional crisis, follow the lead of mindful leaders who turned their crises into opportunities to turn inward and experiment with mindfulness meditation and other transformative practices.
Note: This essay is an excerpt from the forthcoming book, Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders by Denise Frizzell, Ph.D. Denise offers leadership and organizational coaching and consulting for spiritual activists, evolutionaries, progressive change agents and their organizations. Visit https://metamorphosisconsultation.com/schedule-a-coaching-appointment/ to schedule a FREE 20-30 minutes exploratory session.
 We need the compassion and the courage to change the conditions that support our suffering. Those conditions are things like ignorance, bitterness, negligence, clinging, and holding on. Sharon Salzberg
We need the compassion and the courage to change the conditions that support our suffering. Those conditions are things like ignorance, bitterness, negligence, clinging, and holding on. Sharon Salzberg
Jane Dutton and Monica Worline’s book on compassion in the workplace, Awakening Compassion at Work, offers a helpful lens in which to think about the significance of our seventh developmental theme of mindful leaders, self-other empathy and compassion. They equate empathy with compassion, the feeling of “suffering with” another person in a way that emotionally connects and elicits a compassionate response. It is important to note that self-compassion is an essential element of empathy and compassion toward others as it is extremely difficult to give to others that which you do not give to yourself.
Dutton and Worline’s research indicates that employees who experience empathy and compassion from managers-leaders and the organizational context via culture, climate, structure, etc. feel seen and affirmed in their pain and thus bounce back more quickly with increasing satisfaction and organizational commitment. Furthermore, employees have more constructive emotions in the workplace while exhibiting more supportive behavior toward other stakeholders. Therefore, the growing empathy and compassion of mindful leaders act as a positive contagion in the workplace on the employee and organizational levels as illustrated in the following narratives.
Another thing is just a kind of emotional empathy. Like I think I’m much better able to read emotional states. I’m still working on that, but a lot of times I can very quickly pick up on, ‘Oh, this person is distraught right now. I can’t really come down on them about some technical question. I need to, like, address their personal issues.’ And, so that empathy is, again, something that builds very naturally. (Male middle manager and professor)
I’ve used mindful self-compassion prior to some very difficult conversations that I’ve had to have with team members. Sometimes performance improvement kinds of conversations. And looking at how can I as a leader be as empathetic as possible when I’m delivering, say, a complaint that’s been shared by a patient or a family member or even an employee to an employee kind of thing. (Male middle manager in the healthcare industry)
It is different now. I mean now, it is part of my life and I have gained so much wisdom along the way and I have noticed so much about myself which helps me see in that in other people. I can see when other people are stuck in the stress cycle and I am not taking it personally. I am able to bring some compassion to them and some kindness and help calm them even though they don’t know I am doing that. So we come to a space where we can problem solve together. (Female entrepreneur and former healthcare senior executive)
Some of us may not view empathy and compassion as significant qualities of organizational managers-leaders or for our workplaces. However, the mindful leaders in my 2015 study, as well as a growing body of research to include the work of Wolin and Dutton, indicate differently. These two lines of scholarship (mindful and compassionate leadership) demonstrate that being able to “stand in another’s shoes” and see as they see and feel as they feel, enhances the subjective states of both the manager-leader and the direct report as it relates to how they feel toward one another and toward their organization. Furthermore, as highlighted above, such positive inner states ripple outward and favorably impact the larger culture, climate, and performance levels.
Note: This essay is an excerpt from the forthcoming book, Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders by Denise Frizzell, Ph.D. Denise offers leader/leadership and organizational coaching and consulting for progressive change agents and organizations. Visit https://metamorphosisconsultation.com/schedule-a-coaching-appointment/ to schedule a FREE 20-30 minutes exploratory session.
There is a criterion by which you can judge whether the thoughts you are thinking and the things you are doing are right for you. The criterion is: Have they brought you inner peace? Peace Pilgrim
 While the term spiritual is used in different ways, I often use the term to refer to a sense of relatedness or connectedness to others, life, and all that is and ever shall be (i.e., God, Spirit, Source, Allah, etc.). Also, my use of the term spiritual includes finding meaning and purpose in a way that contributes or benefits others or life beyond the self.
While the term spiritual is used in different ways, I often use the term to refer to a sense of relatedness or connectedness to others, life, and all that is and ever shall be (i.e., God, Spirit, Source, Allah, etc.). Also, my use of the term spiritual includes finding meaning and purpose in a way that contributes or benefits others or life beyond the self.
Cindy Wigglesworth, in her 2014 book, SQ 21: The 21 Skills of Spiritual Intelligence, expands this working definition to include a sense of inner calm and peace regardless of circumstances, internal or external while also having a sense of relatedness to life in all its diverse expressions. Wigglesworth proposed that spiritual intelligence (SQ), along with intelligence quotient (IQ), emotional intelligence (EQ), and physical/kinesthetic intelligence, is a core intelligence for living a healthy and fulfilling life in the 21st century.
Wigglesworth’s proclamation about the essential nature of SQ in the 21st century is highly significant for individual leaders and organizations given that the topic of spirituality is often undiscussable in the work environment. Interestingly, the mindful leaders in my 2015 study identified the dimension of SQ, greater inner calm and peace, as well as the increased capacity to tolerate uncertainty (Theme 10) as a result of their mindfulness practice as demonstrated in the following narratives.
It’s interesting, through a downsizing, I started practicing (mindfulness meditation) formally, approximately 2, 2 and a half years ago, almost 3. In the middle of that time period, we had a major reshuffle or reorganization by my employer, so my role expanded in size by about 40 to 50% of what it was previously. So we had two smaller departments, the two were merged and became one super department. We still had the same amount of hours in a day to get the work done, still the same amount of limited resources, however, I found that that through mindfulness I’m able to better handle and focus on the different tasks that are coming at me at any given time. I’m able to free my mind to keep that calm atmosphere and a particular focus on the paths [projects] given, and I’m also able to complete more tasks in a more timely manner. (Male middle manager working in higher education in New Zealand)
I think too there’s a sense of peace you get when you meditate. It really is a stress reducer and anxiety reducer. And, I don’t know if you [have to] do (experience) that necessarily….but it’s a really nice byproduct that I think allows you to be a better leader. (Female middle manager and marketing researcher)
Oh, there is a much bigger sense of calm for me because there is time. There isn’t as much frantic energy being expended. It is a lot more–softer. It’s not a hard push. There is an acceptance, a peace around it that I know the resolution will come. Let’s just give it the time and the opportunity and staying with it. (Female senior manager in information technology).
Perhaps, we can borrow from Peace Pilgrim’s quote at the beginning of this essay and extrapolate that the criterion by which you can determine if a developmental practice is right for you is: Has it brought you greater inner calm and peace? For the 20 mindful leaders in this 2015 study, the answer is yes and perhaps unbeknownst to them, all the while cultivating spiritual intelligence!
Note: This essay is an excerpt from the forthcoming book, Ten Developmental Themes of Mindful Leaders by Denise Frizzell, Ph.D. Denise offers leader/leadership and organizational coaching and consulting for progressive change agents and organizations. Visit https://metamorphosisconsultation.com/schedule-a-coaching-appointment/ to schedule a FREE exploratory appointment.